Translations
| Code | Language | Translator | Run | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | id | id |  |
|
Software Requirements
| Android | iOS | Windows | MacOS | |
| with best with | Chrome | Chrome | Chrome | Chrome |
| support full-screen? | Yes. Chrome/Opera No. Firefox/ Samsung Internet | Not yet | Yes | Yes |
| cannot work on | some mobile browser that don't understand JavaScript such as..... | cannot work on Internet Explorer 9 and below |
Credits

 Fu-Kwun Hwang; Loo Kang Wee
Fu-Kwun Hwang; Loo Kang Wee
end faq
Apps

https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.ionicframework.blocktiltapp658507
Introduction
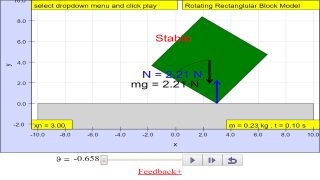
Property of a body for which a small angular displacement set up a restoring torque that tends to return the body to its original position. In a rotational mechanical equilibrium the angular momentum of the object is conserved and the net torque is zero. An important property of systems at mechanical equilibrium is their stability.
Instruction
Drag the center of the block to make the block tilt with an angle. As long as the center of gravity stay inside the surface area of the object on the ground, the block will not fall out. Because the torque will always turn it back.
However, if the center of gravity was outside the surface area, the block will fall out.! You can also change width or height (resize) of the block within the simulation.
Key inquiry question: What are the characteristics and effects of forces in nature? 4. & 6. Turning effects of forces and Equilibrium of forces
• The moment of a force (or torque) = force x perpendicular distance from the pivot. The moment of a force is used in simple machines like the lever.
• Principle of moments states that for a body to be in rotational equilibrium, the sum of its clockwise moments about any point is equal to the sum of anticlockwise moments about the same point.
Key inquiry question: What are the characteristics and effects of forces in nature? 5 Centre of gravity and Stability
• The weight of a body may be taken as acting at a single point known as its centre of gravity; the position of which affects the stability of the body.
• Stability is a measure of a body’s ability to maintain its original position. Objects may be made more stable by lowering its centre of gravity or increasing its base area.
Sample Learning Goals
[text]
For Teachers
[text]
Research
[text]
Video
How to Teach using Simulation Full HD video by Joseph Chua Pei Hwa Sec
How to Teach using Simulation part 1/2 by Joseph Chua Pei Hwa Sec
Video showing how to use effect of forces for mouse trap design
How to Teach using Simulation part 2/2 by Joseph Chua Pei Hwa Sec
Version:
- http://weelookang.blogspot.sg/2016/03/rotating-rectangular-block-model.html a remix by lookang
- http://www.phy.ntnu.edu.tw/ntnujava/index.php?topic=433.0 original Java simulation by Fu-Kwun Hwang
Other Resources
https://www.geogebra.org/m/xmx55cj5 by seng kwang
https://ggbm.at/qszfx35k by tan seng kwang
https://ggbm.at/sw3txavd by Vincent Lew and tan seng kwang